Before we start, there is one golden rule: Don't guess. Optimization is great, but it adds complexity. You should only start optimizing after you have proven, through load testing, that a specific part of your system is actually slow.
Once you know where the problem is, here is how you can fix it.
1. Use Caching
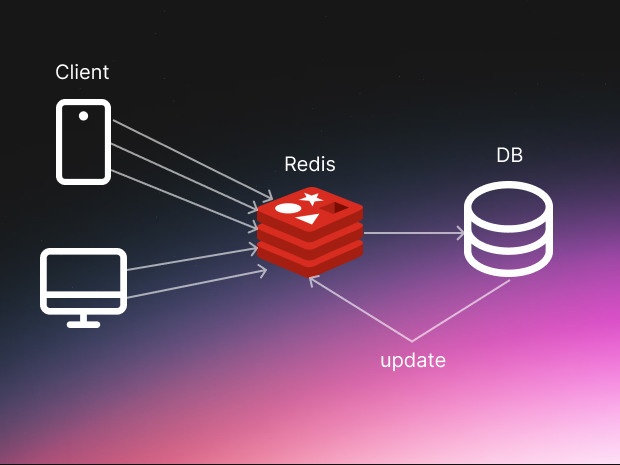
This is often the easiest win. Caching means saving the result of a hard job so you don't have to do it again.
Imagine your API calculates a complex report. If the data hasn't changed, why calculate it again for the next user? Just save the answer in a fast storage system like Redis or Memcached. Even caching data for a few seconds can make a huge difference in speed because you are skipping the heavy lifting entirely.
Simply, without calling the database every time when new request comes in, we can check if the query exists in our caching layer and return from there without going to the database. It's really simple in every language and framework. For example in nodejs:
if (redis_client.has(key)) {
return redis_client.get(key);
} else {
const result = await db.query(key);
redis_client.set(keyof, result);
return result;
}
2. Connection Pooling
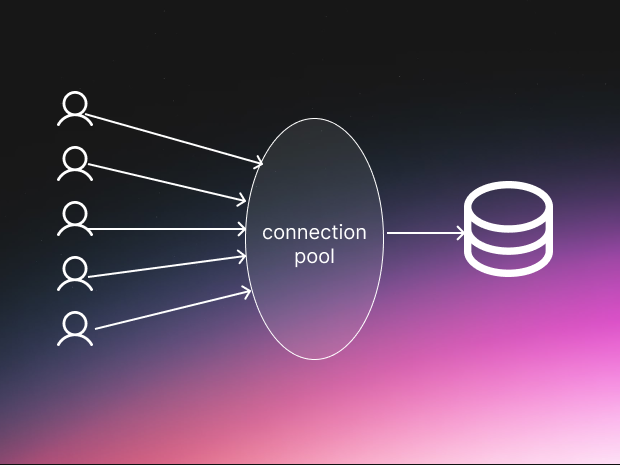
Opening a new connection to a database takes time. It involves "handshakes" and setup protocols that slow you down.
Instead of opening and closing a connection for every single user request, keep a "pool" of open connections ready to go. When a request comes in, it borrows a connection, uses it, and returns it to the pool.
Note for serverless users: If you use tools like AWS Lambda, this is harder because they scale rapidly. You might need specific tools like AWS RDS Proxy to manage these connections for you so you don't overwhelm your database.
3. Avoid the N+1 Problem
This is a classic mistake that kills performance. Let's say you want to show a list of blog posts and their comments.
- The Bad Way: You run 1 query to get the posts. Then, for each post, you run another query to get its comments. If you have 100 posts, that is 101 queries!
- The Good Way: Run one query for the posts, and one query for all the comments. That is just 2 queries.
Reducing the number of trips to your database is one of the best ways to improve performance.
4. Use Pagination
Never try to send everything at once. If your API tries to return 10,000 items in a single request, it will be slow for everyone.
Break the data into small chunks, or "pages." Use limits and offsets to only send what the user needs right now. This makes the data transfer faster and reduces the load on your server significantly.
5. Fast JSON Serializers
APIs usually talk in JSON text. Converting your code's data into this text format is called "serialization."
Believe it or not, some default libraries are much slower at this than others. If you switch to a lightweight, fast serialization library meant for high performance, you can shave precious milliseconds off every single request without changing any logic.
6. Enable Compression
Big files take longer to download. You can shrink your API responses using compression tools like GZIP or Brotli.
This works like a zipper for your data. Your server zips it up, sends it quickly over the network, and the user's device unzips it. Many networks (CDNs) like Cloudflare can even do this for you automatically. It reduces the payload size, making the internet feel faster.
7. Asynchronous Logging
Writing logs (records of what happened) takes a tiny bit of time. But in a busy system, those tiny bits add up.
Instead of making the user wait while your system writes a log to a file, use asynchronous logging.
- How it works: Your main program throws the log message into a temporary memory buffer and immediately moves on. A separate background process picks it up and writes it to the file later.
- The trade-off: If your system crashes completely, you might lose the logs that were waiting in the buffer. But for the speed gain, it is often worth the risk.
Summary
Making an API fast isn't magic. It is about being smart with your resources. By caching data, managing connections, and sending smaller packages, you can make your application feel 10x faster.
Go explore your code and see which of these you can use today!